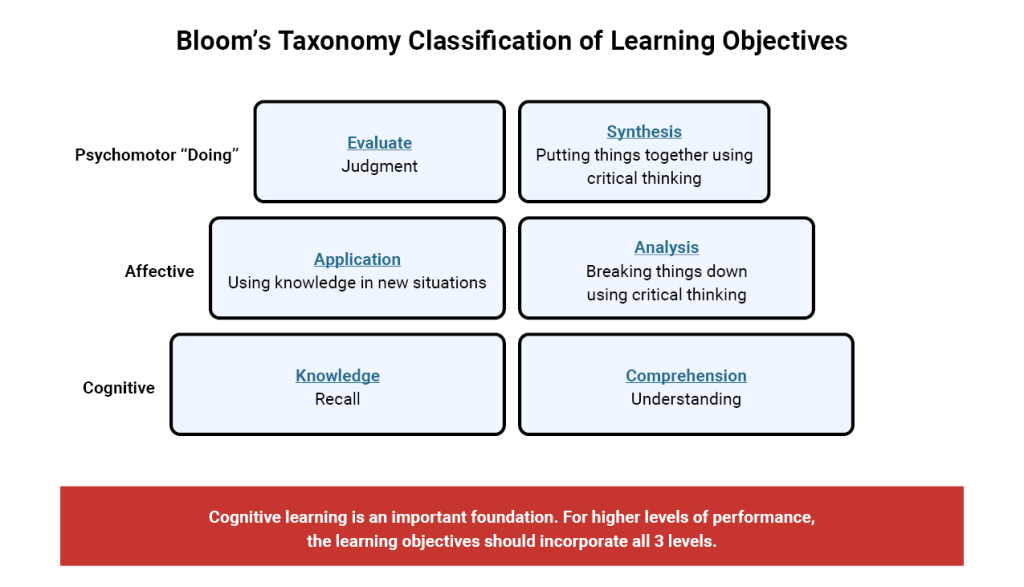
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a classification of the different objectives that educators set for its students. It divides the objectives into 3 levels of learning: Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor. These levels are further divided into 6 categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Evaluation and Synthesis.
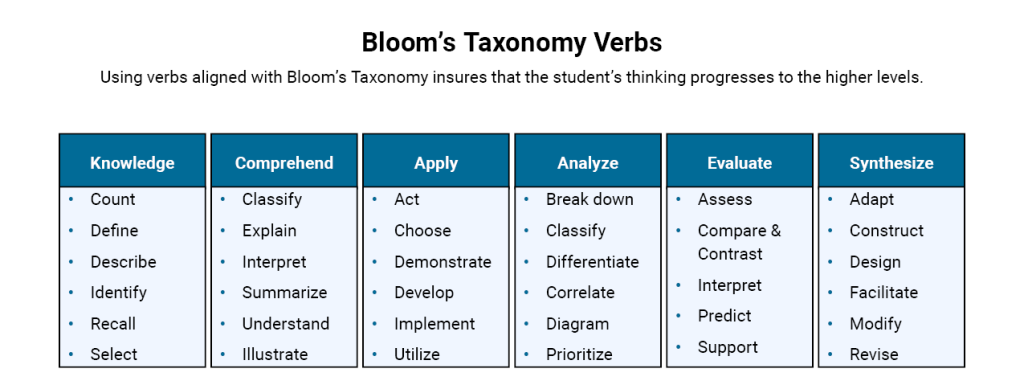
One of the goals of Bloom’s Taxonomy is to encourage educators to incorporate all 3 levels into their courses, creating a more holistic form of education. Bloom’s uses verbs rather than nouns to describe the objectives and the verbs are intended to be feasible and measurable. Depending on the verb the educator must identify the best learning strategy to aid the student in reaching the objective.
Example
You are a student that is enrolled in a French Cooking course. Your goal for the course is to learn to cook French meals. Let’s look a few possible learning objectives. Upon completion of this French Cooking Course you will be able to:
- Write a French recipe
As a learner, do you think this course will ensure you reach your goal? Probably not. Why not? Because the course is offering cognitive (Level 1) understanding but the learning objectives don’t include application (Level 2). So what if we add:
- Prepare a French recipe
How about now? We are getting closer. You definitely want to prepare a French recipe in the course, but we are still missing a vital component of a course like this:
- Create a French recipe of your own
- Evaluate the 3 key qualities found in French cuisine
Now this is a course that can help you reach your goal. Upon completion you should be able to understand how to cook French cuisine (cognitive), be prepared to cook French cuisine (affective) and have the tools to assess the quality of the food you prepare (psychomotor).
The 6 Categories of Blooms Taxonomy
| Knowledge Memory of learned materials. | Comprehension Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas. | Application Using acquired knowledge to solve problems in new situations. |
| Analysis Examine and breaking information into parts by identifying motives and causes. | Evaluation Present and defend opinions by making judgments. | Synthesis Compile the information in new ways or proposing alternative solutions. |
Bloom’s Taxonomy and Learning Objectives Published by Acuity Institute
